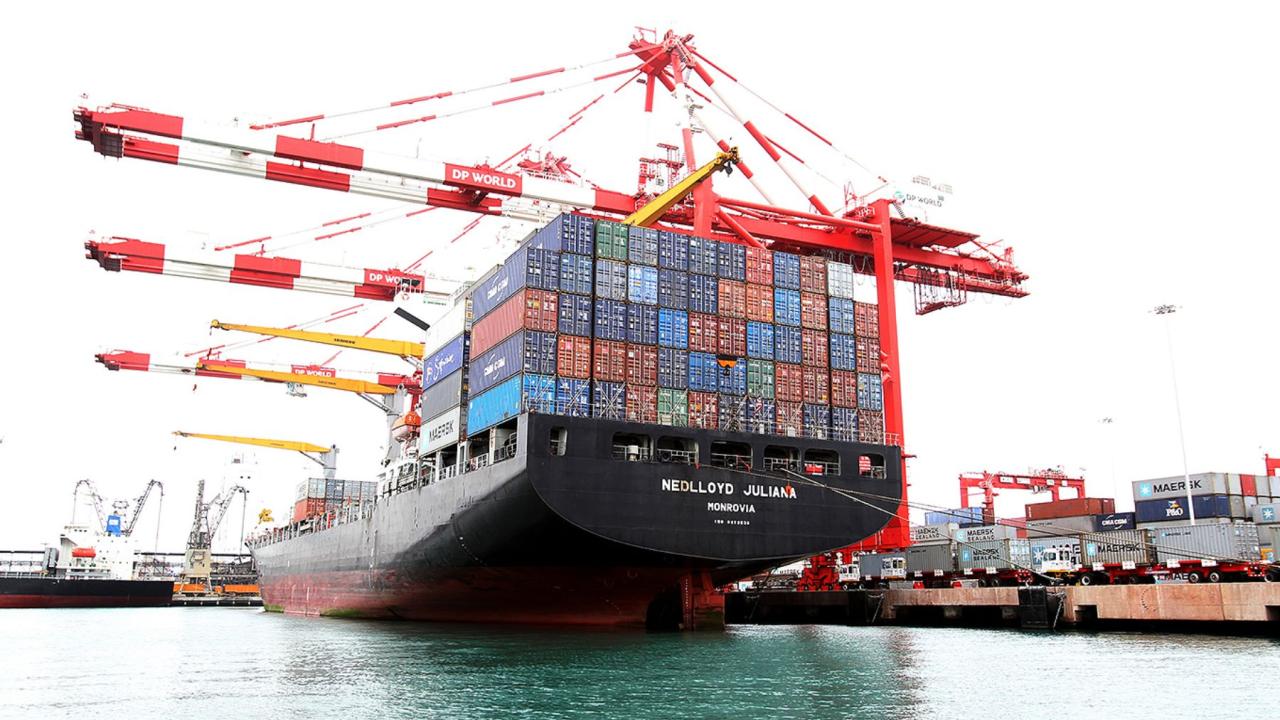
According to the report from the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), the region's foreign sales showed a year-on-year increase of 1.3%, partially reversing the contraction observed in 2023.
The foreign trade of Latin America (LA) in the first quarter of this year registers a complex and challenging panorama, because although a slight recovery is observed in total shipments, there are significant differences between subregions, countries and sectors.
According to a recently published report from the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), foreign sales in the Latin American region showed an interannual increase of 1.3%, between January and March 2024, partially reversing the contraction of 1.3%. % observed in 2023, indicates a report published in the Económika Supplement of the Diario El Peruano.
This rebound, although modest, illuminates a faint light of hope in a complex and uncertain global panorama. However, it is crucial to analyze this growth with caution, since it hides diverse realities and presents great challenges for the region.
Performance
South America, the largest area and with the greatest weight in exports in the region, experienced an increase of 1.9% in its exports during the first quarter of 2024. This rebound is mainly due to the growth in exported volumes (8.3 %), which reflects greater productive activity and a better supply capacity of the countries in the region.
However, the behavior of commodity prices was mixed. Some items such as coffee experienced a significant increase, driven by high demand and shortage of supply in the international market. On the other hand, other products, such as soybeans and iron ore, recorded falls, which negatively affected the income of exporting countries.
In the case of Peru, in the first quarter of 2024, shipments abroad reached US$ 15,828 million, which represents an increase of 3.5% compared to the same period of the previous year.
This favorable result is largely due to the proactive trade policy implemented by the Peruvian Government, focused on opening markets and strengthening the competitiveness of the export sector.
The head of the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism (Mincetur), Elizabeth Galdo, highlighted the importance of this long-term policy, noting that “it has a positive impact on the national economy.”
The current trade agreements with 58 countries opened new opportunities for Peruvian exporters, diversifying destination markets and increasing demand for Peruvian products abroad.
Deceleration
According to the IDB report, Mesoamerica as a whole showed a more modest 0.7% growth in its exports during the first quarter of 2024, representing a sharp slowdown compared to the 2.3% recorded in 2023.
Mexico, the main player in the region, experienced a 1.7% increase in its exports, driven mainly by the growth of sales to the United States and the rebound in prices in some sectors such as fruit and vegetable and automotive. However, this growth was not enough to compensate for the drop in Central American exports, which as a whole contracted by 7.1%.
Costa Rica was the only Central American country that registered positive growth in its exports during the first quarter of 2024, although less than the previous year. This performance was aided by increased sales to China, reflecting the growing importance of this market for the region.
Target markets
Latin American exports are concentrated in three large markets: the United States, China and the European Union. However, the dynamics of exports to these destinations were contrasting during the first quarter of 2024.
Sales to the United States from Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) grew 3.4% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2024, while total imports from that country increased only 0.7%.
LAC gained market share in US purchases, going from 18.3% in 2022 to 20% in 2023. This positive trend continued in the first quarter of 2024, reflecting the importance of the United States as a market for the region.
In the case of China as a destination for LAC shipments, these increased 4.7% in 2023, while total purchases from China fell 5.6%. The region's share of the Chinese market increased from 8.6% in 2022 to 9.5% in 2023. The growth trend continued in the first quarter of 2024, with exports increasing by 9.2 %.
This positive performance is mainly due to China's growing demand for commodities and manufacturing in the region.
In contrast to the two previous markets, exports to the European Union (EU) from LAC fell 6.8% in 2023, while total imports from that area decreased 5.7%. ALC's share of the European market fell from 1.9% to 1.8% of total imports.
Perspectives
While the region's export trend appears to have changed direction, it is still too early to determine whether it is a sustained rebound. The high volatility of commodity prices and the uncertain outlook for global demand create a challenging outlook for Latin America.
Leading indicators show asymmetric trends and depend largely on the policies implemented in the coming months. The war in Ukraine, sanctions against Russia, the slowdown of the Chinese economy and geopolitical tensions in general create an environment of uncertainty that makes it difficult to predict the future behavior of international trade.
In this context, Latin America faces important challenges to consolidate its trade recovery and achieve sustained and inclusive economic growth.
In the case of Peru, in the first quarter of 2024, shipments abroad reached US$ 15,828 million, an increase of 3.5%.
Leading Indicators
The IDB notes that although the region's export trend appears to have changed direction, it is still too early to determine whether it is a sustained rebound.
The high volatility of commodity prices, the uncertain outlook for global demand and geopolitical tensions generate a challenging outlook for Latin America's foreign trade.
Leading indicators show asymmetric trends and depend largely on the policies implemented in the coming months. Additionally, the war in Ukraine and sanctions imposed on Russia have created disruptions in supply chains and increased energy and food prices, negatively affecting international trade.
In this context, Latin America faces important challenges to consolidate the recovery of foreign trade and achieve sustained and inclusive economic growth.