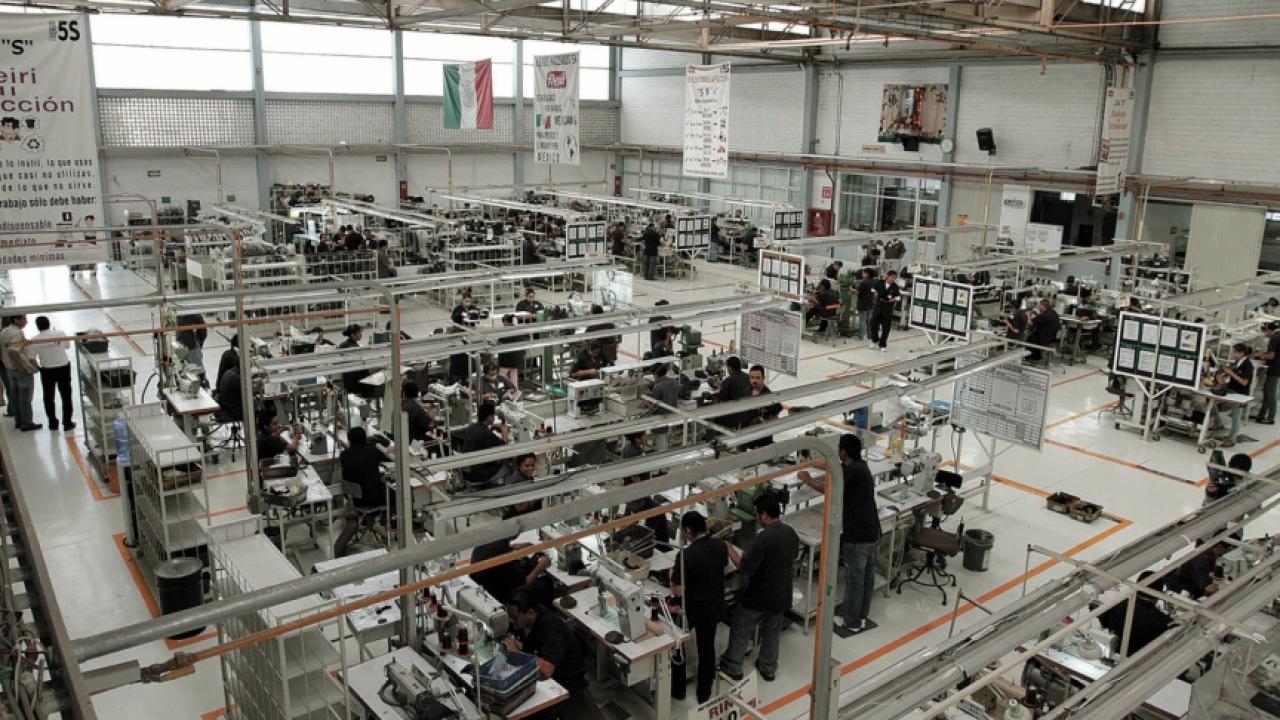
The close link between manufacturing and US economic activity, which also showed signs of slowing, negatively affected regional production chains, business leaders agreed.
During the second quarter of the year, manufacturing activity in Mexico had its largest contraction in the northern region (-2.6%) compared to the same period in 2023. It was followed by the central-northern (-1.2%), central (-0.7%) and southern (-0.4%) regions; that is, manufacturing production in the Aztec country accumulated four consecutive quarterly reductions, showing a weak performance, reported the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) in its most recent Report on regional economies.
In the northern, central-northern and central regions, manufacturing activity continued on a downward trajectory in the second quarter of 2024. This contraction was mainly influenced by the weakness in both domestic and foreign production.
The close link between manufacturing and economic activity in the United States, which also showed signs of slowing, negatively affected regional production chains, according to business leaders from these regions consulted by Banxico.
Despite the improvement observed in light vehicle production in June, this progress was marginal and could be temporary, since production levels returned to low levels in July. In addition, the difficulty in filling vacancies and high levels of staff turnover continue to be limiting factors in the region, although their intensity has decreased compared to previous quarters.
On the positive side, the relocation of production lines from Asia continues to be beneficial, as does the depreciation of the peso against the dollar, which has helped improve profit margins.
IMPACT OF NEARSHORING
12.9% of companies with more than 100 employees reported an increase in their production, sales or investment during the period from July 2023 to July 2024, in relation to the relocation of companies, highlights the Banxico analysis.
The northern region, with a close commercial relationship with the United States, had the highest percentage of companies benefiting from nearshoring , with 16.9%, which is attributed to its geographic proximity and its strong integration into global value chains; the manufacturing sector in the region was the most favored, with an increase in production and greater investment in infrastructure and personnel, reflecting the attraction of foreign investment.
In the north-central region, 13.2% of companies experienced positive effects from nearshoring , and the arrival of production lines from Asia increased, favored by trade agreements with the United States and Canada.
The central region recorded an increase of 11.4%; both the manufacturing and non-manufacturing sectors reported benefits, although subsectors with less integration into global chains showed limited growth. The proximity to the capital and the development of infrastructure could consolidate its position in the future.
Southern Mexico reported the lowest percentage of companies benefiting, with 7.8%. Factors such as poor infrastructure and lack of connectivity restricted their ability to take full advantage of the phenomenon. With these obstacles overcome, the region could experience greater growth in the coming years.
Despite the current benefits of relocation, 41.3% of companies anticipate that its greatest impact will materialize between 2026 and 2030. Proximity to the United States is the most relevant factor for consolidating nearshoring, along with trade agreements, technological innovation, and the macroeconomic environment. However, limitations such as energy supply must be addressed to consolidate Mexico as a destination.