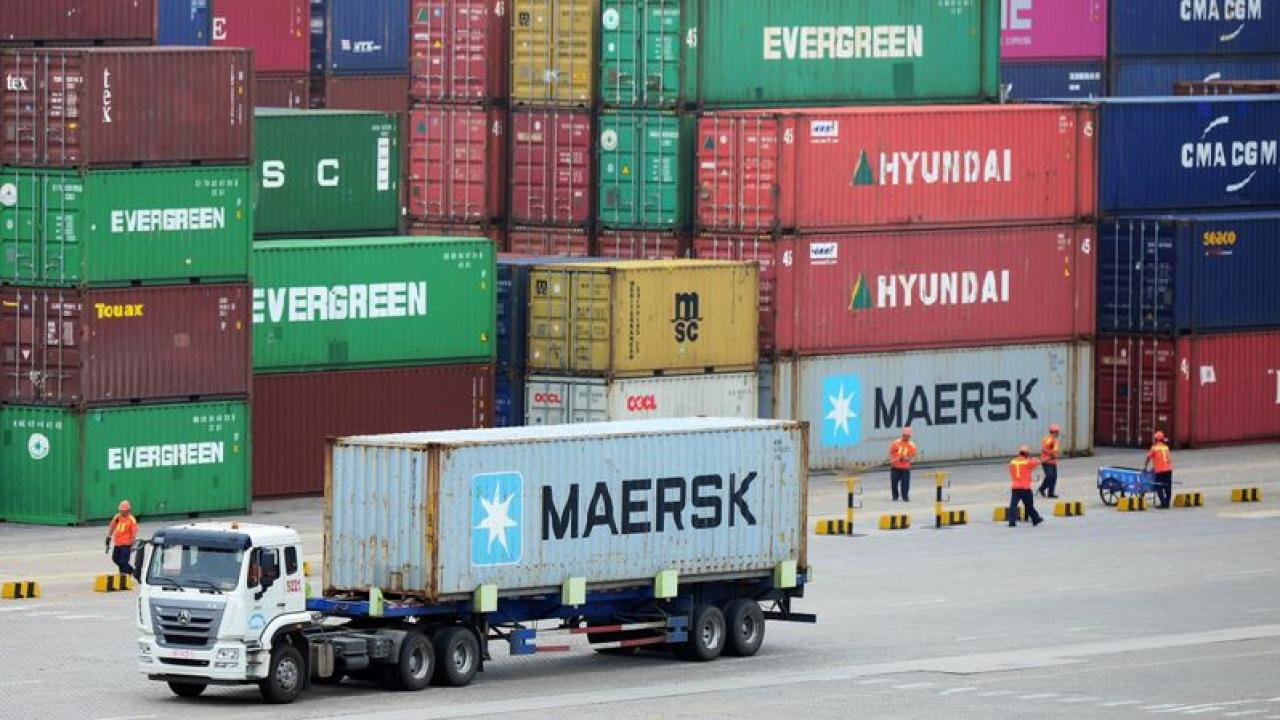
In 2023, the negative balance in the US merchandise balance increased 117.9% with Mexico compared to 2017 (the year before the start of the trade conflict between China and the United States). It also registered an increase with Canada (234.3%) and Vietnam (170.9%).
In 2023, the United States increased its trade deficit in products with Canada and Mexico, its partners in the T-MEC, and with Vietnam at triple-digit rates compared to 2017, the year before the trade war that that power has with China.
Considering the period of the last six years, the negative balance in the US merchandise balance increased 234.3% with Canada (-US$ 78,353 million), 170.9% with Vietnam (-US$ 109,129 million) and 117.9 % with Mexico (-US$ 156,854 million).
The United States' global trade deficit reflects that this country consumes more than it produces and imports more than it exports.
On the contrary, the negative balance in the US trade balance of products decreased with China 24.1% between 2017 and 2023, to US$300.23 billion, according to data from the Department of Commerce.
One of the main critics of the United States trade deficit was Donald Trump, from when he was a presidential candidate and then as President.
“Since the adoption of NAFTA, the United States has accumulated trade deficits totaling more than $2 trillion (and it is a much larger number) with Canada and Mexico,” Trump said at the White House in 2018, speaking about the T -MEC. “They make cars. They make products. They do everything in another country. They send them to the United States, without taxes.”
But according to an analysis by the US Congress, most economists argue that the trade deficit is largely due to US macroeconomic policies, mainly an imbalance between domestic savings and total investment in the economy.
The most important cause of the trade deficit is the low domestic savings rate of households, businesses, and the government in the United States relative to their investment needs.
To make up for that shortfall, Americans must borrow from overseas countries (like China) with excess savings.
This borrowing allows Americans to enjoy a higher rate of economic growth than the United States would obtain if it had to rely solely on domestic savings. This boosts American consumption and import demand, producing a trade deficit.
Several other factors can affect the size of the United States trade deficit in the short term, such as differences in economic growth between countries.
The role of the dollar is also an important factor in sustaining the US trade deficit. As the de facto global reserve currency, the US dollar facilitates trade deficits by expanding the availability of dollars and dollar-denominated assets.
Foreign investors seek out dollar-denominated assets as safe haven assets, especially in times of economic stress.
As long as foreigners (both governments and private entities) are willing to lend the United States funds to finance the lack of savings in the US economy, for example by purchasing US Treasury securities, the trade deficit can continue, it concludes. analysis.
Broadly speaking, a trade deficit is an indicator that a nation consumes more than it produces and does not save enough domestically to finance its investment needs. The United States has run trade deficits annually for most of the post-World War II period.